Series: GT-CP Video Tutorial
Noritake GT-CP Tutorial | Part 3: Save and Recall Image with GTOP
Table of Contents
Last update: April 9, 2019
This web-page is intended as a text supplement for the video above. This page will provide all of the necessary information (web links, images, etc.) to achieve the goals accomplished in the video tutorial.
Overview
In this video we’re going to save an image to the GT-CP’s FROM2 and then recall that image to the display.
Note:
Following along from part 2 , we used lighthouse.jpg and previewed that image onto the module. We’re going to use this same image and save it to the module’s FROM2 and then recall it.
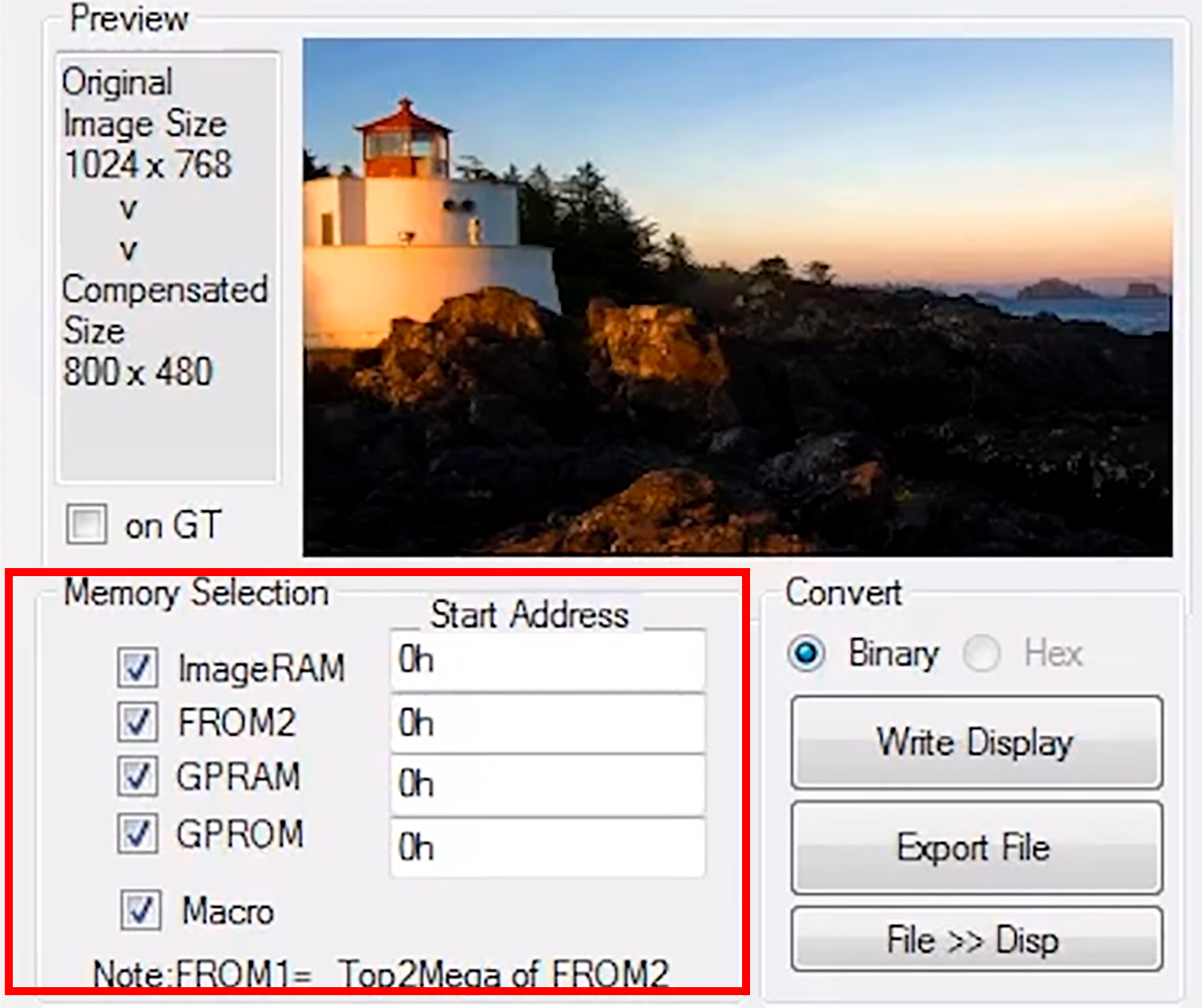
Write to FROM2
We already have lighthouse.jpg in the FROM2 node. So we need to go down to memory selection and look at the start address. We’re gonna make this simple and keep the start address at 0.
Note:
A different start address can be used if you’re trying to avoid certain sections of FROM2
So, next we can hit “Write Display”. Even though we have all memory options checked, the tool will only write to FROM2 because nothing else is in any of these other memory nodes.
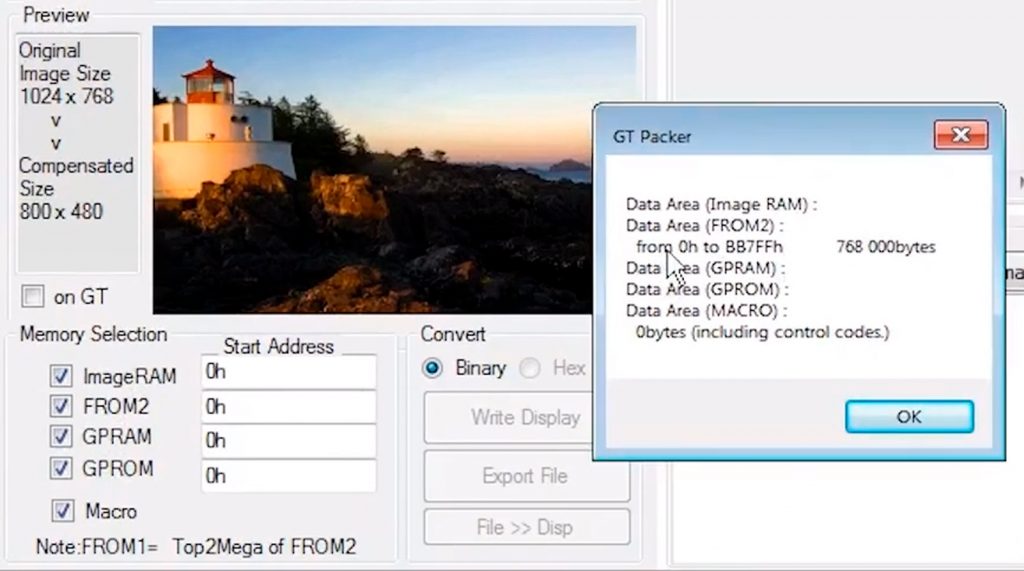
In the resulting pop-up window, you can see the start and end address and the number of bytes being written.
Hit OK. Then it will write the image data to the module.
We’ll see this bit of extra information on the right side in the map area pop-up.
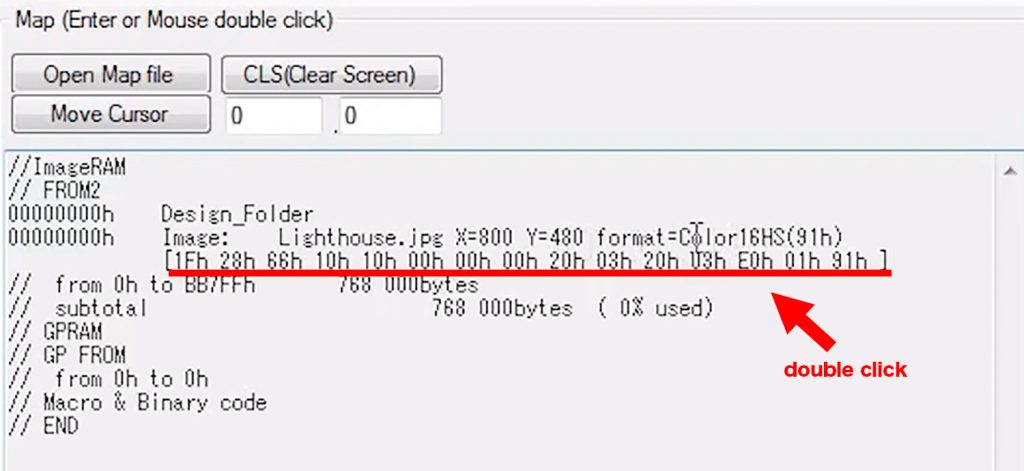
We can see at address 0, the lighthouse image is saved with a resolution of 800×480 in a 16-bit high-speed color format.
Additionally, there is a byte sequence down below here. This sequence will recall the image from FROM2 to the display.
This byte command is specifically tailored for the image that was saved. If I double click on this, this byte sequence will be sent to the module via the USB cord.
Recall Image
So, let’s double click and the image is immediately recalled and shown on the display.
It’s very fast because the image is being recalled from FROM2 and not being sent through the USB cord.
The only data being sent through the USB cord is the image recall command.